
Source: https://unsplash.com/photos/nFumIdf3IHE
For a quick hemp textile industry overview, let’s start with some numbers.
- The global hemp clothing market is valued at $5.66 billion as of 2021.
- The number is expected to reach $7.91 billion by 2022 and $26.41 billion by the end of 2026.
- This valuation registers a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 39.7% during the forecast period of 2021-2022.
But numbers can be confusing.
So, here’s something even better.
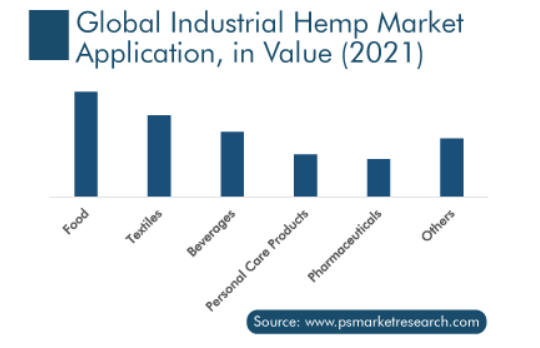
What do you see here?
It’s the plain truth; hemp textiles are the second biggest category within the hemp industry.
One thing is clear.
The hemp textile segment is simmering with excitement and potential. More industrial leaders acknowledge the future and impact of hemp.
But the industry is still at its nascent stage. It must overcome a litany of issues before it grows into a mature market. Problems like a disjointed supply chain, unreliable sourcing, and untested techniques still lie heavy in the industry.
Hemp Textiles: An Industry Overview
Industrial hemp farming regulations have shifted over the past few years.
So, how did this exactly happen, and why?
The demand for natural and organic products has skyrocketed in recent years. That’s one of the major factors behind the growing hemp textile market.
The younger generations are demanding more environmentally responsible and sustainable fashion options. That leaves businesses choosing to harness this super plant as a substitute for cotton and synthetics.

To give you an overview of the industrial hemp market, here are a few quick highlights:
- Developed countries like the US, UK and Canada are creating and updating licensing structures for the cultivation, and processing of industrial hemp.
- In 2021, the French market was the highest contributor of revenue from industrial hemp.
- From 2015 to 2019, Europe increased the allocated hemp farming area from 20,000 hectares to 35,000 hectares.
- Hemp production shot by 65% from 95,000 tonnes to 155,000 tonnes in Europe in the years 2015 to 2019.
- The United States removed hemp with THC levels less than 0.3% from the Controlled Substances Act.
- In 2021, the European industrial hemp market had the highest revenue share of 35%.
- China exports over 2 million metres of hemp textiles in a year.
Global Hemp Textile Market: Outlook For Farmers
Hemp is an exceptional crop in terms of strength and environment-friendliness. This creates a massive demand for it in the textile industry.
More than 32 countries, including Canada, the United States, China, France, and the United Kingdom, have adopted industrial hemp for textiles. China is the largest producer of hemp textiles.
As leading industries come into play, the global hemp textile market is expected to reach $63.04 billion by 2029, a 32% CAGR from 2021-2029.
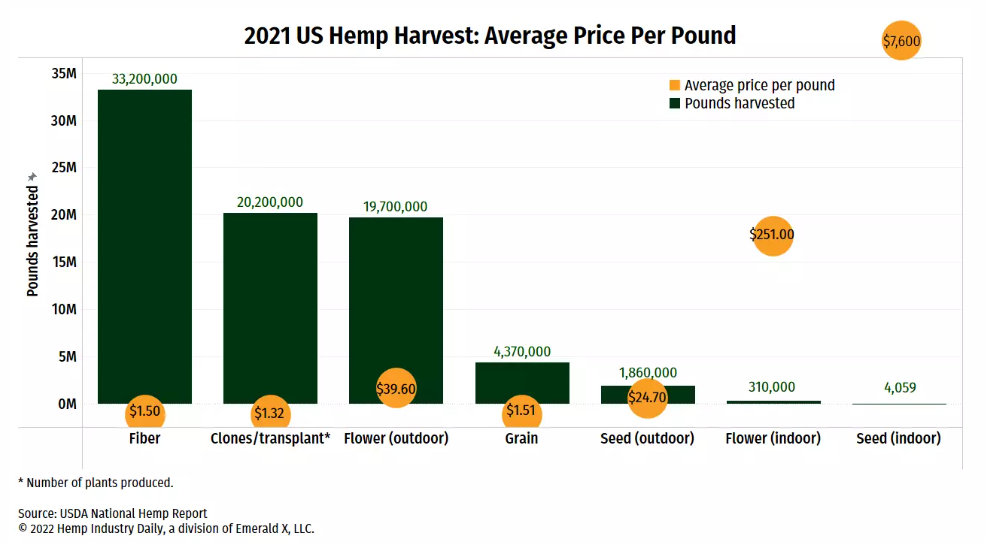
But what’s in it for the farmers?
Those growing hemp fibers call it a great rotational crop. It can be substituted for any harvest and takes only about 90-120 days to grow.
If we calculate per acre basis, an estimate shows that hemp farmers make:
- $250-300 – from one acre of hemp and
- $100-200 – from one acre of soybeans or corn.
Do you see the difference?
India stands at the top for overall industrial hemp production. It has relatively looser laws around hemp production compared to the United States.
However, only one state (Uttarakhand) has developed policies for researching, growing, and cultivating industrial hemp.
Hemp Textile Market Segments
The global hemp textile market can be segmented into 4 broad spectrums – type, distribution channel, end-user, and region. The market is categorized into different products and supply channels based on each segment.
By Type
The ‘type’ segment categorizes the market into different garment types, including pants, shirts, activewear, innerwear, thermals, and others.
As per the market, this segment has been the highest contributor to the global hemp textile numbers, with an estimated $485.6 billion in 2021.
By Distribution Channel
The ‘distribution channel’ segment can be divided into online sales channels, retail stores, hypermarkets, and supermarkets.
This is also one of the most important segments in the hemp textile industry, where online sales and retail stores account for almost 70% of the market share in 2021.
By End User
The ‘end user’ spectrum is categorized based on the gender and age of the buyers – men, women, and kids.
During 2021, the women category witnessed higher demand and was the largest contributor to the market. The kids and men categories are also expected to grow over the next few years.
By Region
Considering the ‘region’ segment (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, LAMEA) on a global scale in 2021, North America contributed the highest revenue, followed by Europe.
The market for hemp clothing in North America covers more than 2/5th of the global demand. The key players face steep competition, with new brands developing more advanced sustainable clothing options.
Hemp Textile Production Process
Hemp is a fast grower and reaches an approximate height of 2-4 meters in a span of 90-120 days.

Although hemp does not require any chemical aids and grows organically, the process of making hemp fabric is labour-intensive and time-consuming.
- Manufacturing
Hemp can grow on any kind of soil, but it grows best on ones rich in nitrogen and non-acidic, well-drained, and humid weather.
For large-scale production, hemp harvesting machines are used instead of cutting the plants with a sickle.
Once cut, the stalks are set on the field for retting, allowing the pectin to decay and separate the fiber from the other parts.
The dried fibers are then separated using a decorticator and beaten to take out any impurities from the fibers. This step is followed by hacking the comb that cleans the fibers before final spinning.
- Quality Control
To test the fineness and tensile strength of the fibers, they must go through a series of quality control checks.
For example, recording the THC content of the plant continuously so it does not surpass the government-allowed mark.
The moisture content and color of the fibers should also be noted at every stage.
- Waste and By-products
The remaining hemp fiber can be used to make many different products, including horse bedding, paper, and concrete blocks. Some parts can also be pressed and used as fuel and soil additives.
Challenges of the Hemp Textile industry
Hemp can potentially be used to replace some of the most used fibers for textiles. But it also comes with a set of challenges in terms of governance and fiber processing in the textile industry.
Since hemp is often confused with the psychoactive drug marijuana, there may be some complicated legislation around hemp harvesting and production.
Secondly, the hemp fiber processing can be extensive, and the important steps like retting require massive energy and water input for large-scale production.
Industrial Hemp: Global Market Trends and Drivers
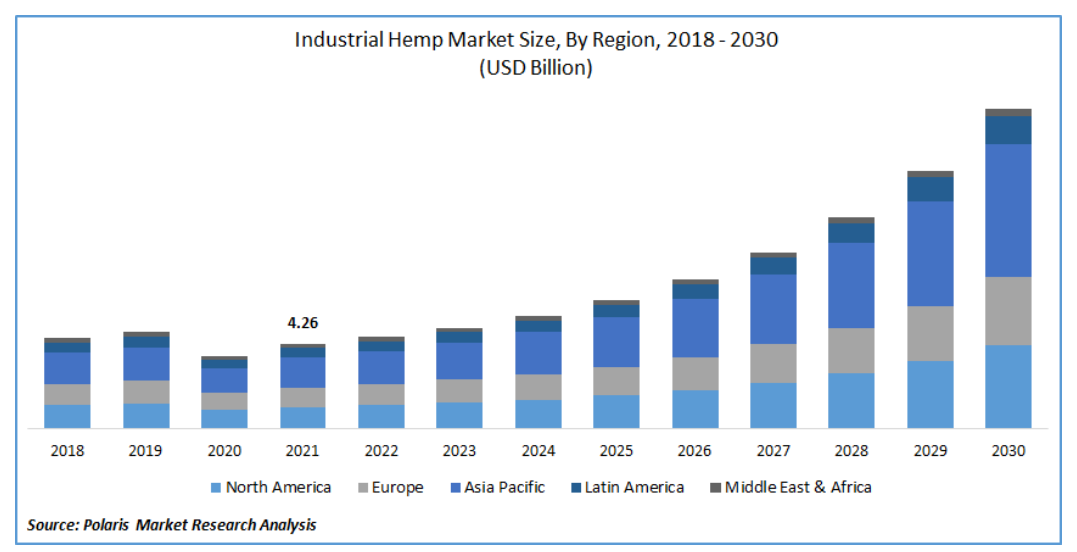
The global market size of industrial hemp has been estimated at $4.13 billion as of 2021, which is expected to rise to $16.75 billion by the end of 2030.
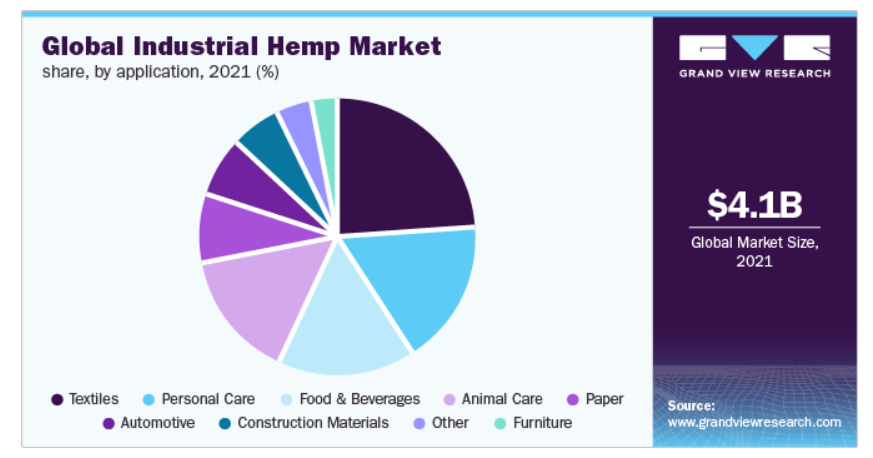
The growing market is driven by the expanding demands and application of industrial hemp. It is in huge demand across sectors, including textile, food and beverage, manufacturing, personal and animal care, and many others.
The major industry leaders are investing heavily in research and development activities to know more about the plant and yield more benefits from its cultivation.
One of the key drivers of the hemp textile market is the environmental impact of growing and processing cotton.
Growing cotton adversely impacts the soil causing soil salinization, water shortages, and also pollution from pesticides. Hemp is the ‘new’ fiber that’s a potential alternative to cotton and is also hugely profitable.
To further refine the harvesting process of hemp, industry stakeholders are investing massively into R&D. It’s also a step to develop new technologies and ways for an improved lineup of hemp varieties.
Benefits of Using Hemp in Textiles
Some of the other common benefits of using hemp in textiles are:
- Reduces carbon footprint: Can be grown without pesticides.
- No heavy irrigation required: Requires less water and lowers the risk of polluting water bodies like lakes, rivers, etc.
- Biodegradable: It can grow in almost any soil type and helps aerate and restore vital nutrients in the soil.
- Requires less land to grow: It can grow up to three times more fiber than cotton for a given piece of land.
- Abrasion-resistant fabric: It is the strongest natural fiber that is not derived from any petrochemicals.
The long-term benefits of using hemp in the textile industry could be well enough to replace cotton and linen.
Linen is considered the closest competing fiber for textiles of hemp. But even then, it’s way more abrasive than hemp in terms of sustainability and eco-friendliness.
Also, because of the changing fashion trends, there’s a potential market for hemp clothing in the coming years.